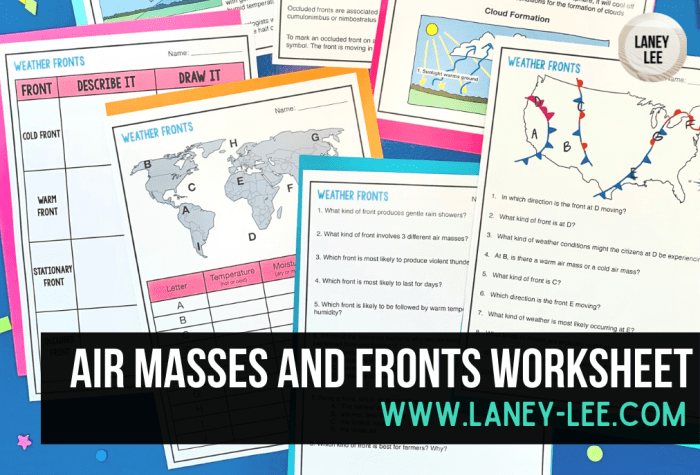
Embark on a meteorological adventure with our air masses and fronts worksheet, where you’ll unravel the intricate tapestry of weather patterns. Dive into the fascinating world of air masses, the building blocks of our atmosphere, and explore how they interact to shape the weather we experience.
From the formation of air masses over diverse regions to their movement and influence on precipitation, clouds, and temperature, this worksheet will guide you through the captivating interplay of these atmospheric giants. Get ready to witness the dynamics of weather fronts, the boundaries where air masses collide, and uncover their role in shaping weather systems and predicting the ever-changing conditions of our planet.
Definition and Classification of Air Masses
Air masses are vast bodies of air that have similar temperature and moisture characteristics. They play a crucial role in determining weather patterns across the globe.
Classification of Air Masses
Air masses are classified based on their temperature and moisture content:
- Polar air masses: Cold and dry, originating from high-latitude regions.
- Tropical air masses: Warm and moist, originating from low-latitude regions.
- Continental air masses: Dry, originating from land areas.
- Maritime air masses: Moist, originating from ocean areas.
Formation and Movement of Air Masses: Air Masses And Fronts Worksheet
Air masses form over extensive areas with relatively uniform temperature and moisture characteristics. The source regions, where air masses originate, play a crucial role in shaping their properties.
Formation of Air Masses, Air masses and fronts worksheet
- Continental Air Masses:Form over landmasses and acquire the characteristics of the surface below. They can be classified as continental polar (cP) or continental tropical (cT), depending on the latitude of their source region.
- Maritime Air Masses:Form over oceans and inherit the moisture and temperature traits of the water surface. They are categorized as maritime polar (mP) or maritime tropical (mT).
Movement of Air Masses
Air masses move primarily due to pressure gradients. High-pressure systems (anticyclones) act as sources of air, while low-pressure systems (cyclones) act as sinks. Air masses flow from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas, following the path of least resistance.
The direction of air mass movement is influenced by several factors, including the Coriolis effect, which deflects moving air to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
Weather Associated with Air Masses
Air masses play a crucial role in shaping weather patterns by influencing temperature, humidity, and precipitation. Different types of air masses are associated with distinct weather conditions.
Role in Precipitation
Air masses can affect precipitation in various ways. Warm, moist air masses, such as maritime tropical (mT) air, often bring heavy rainfall and thunderstorms. Cold, dry air masses, like continental polar (cP) air, typically suppress precipitation due to their lack of moisture.
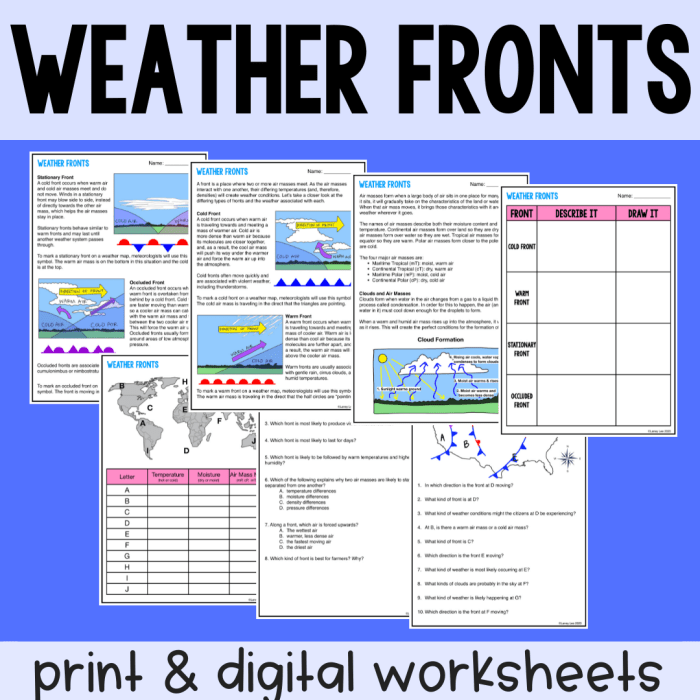
Cloud Formation
The characteristics of air masses influence cloud formation. Stable air masses, like continental polar (cP) air, promote clear skies with few clouds. Unstable air masses, such as maritime tropical (mT) air, favor cloud development and precipitation.
Temperature Changes
Air masses can cause significant temperature changes. Warm air masses, like maritime tropical (mT) air, can raise temperatures and create warm and humid conditions. Cold air masses, such as continental polar (cP) air, can lower temperatures and lead to cold and dry weather.
Fronts
Weather fronts are boundaries between air masses with contrasting properties. They form when two air masses of different temperatures and densities meet.
As the denser air mass pushes against the less dense air mass, the less dense air mass is forced to rise. This rising air cools and condenses, forming clouds and precipitation.
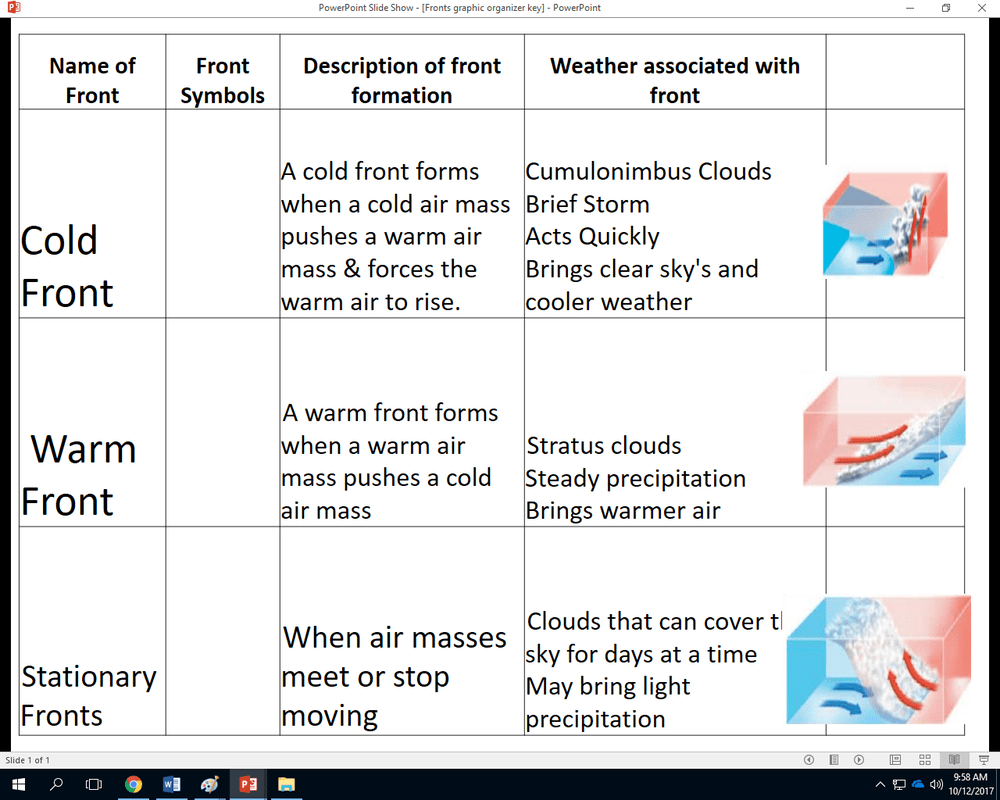
Types of Fronts
- Cold Front:A cold front forms when a cold air mass overtakes a warm air mass. The cold air mass pushes the warm air mass upward, creating a steep slope. Cold fronts are associated with thunderstorms, heavy rain, and strong winds.
- Warm Front:A warm front forms when a warm air mass overtakes a cold air mass. The warm air mass slides up the cold air mass, creating a gentle slope. Warm fronts are associated with light rain or drizzle, and rising temperatures.
- Occluded Front:An occluded front forms when a cold front overtakes a warm front. The cold air mass behind the cold front pushes the warm air mass upward, and the warm air mass is trapped between the two cold air masses. Occluded fronts are associated with prolonged precipitation and fog.
- Stationary Front:A stationary front forms when two air masses meet and neither is able to advance. Stationary fronts are associated with stable weather conditions, such as clouds and light rain.
Fronts and Cyclogenesis
Fronts are boundaries between air masses with different temperatures and densities. They play a significant role in the development of cyclones and anticyclones, which are large-scale weather systems that influence weather patterns.
If you’re looking for a different kind of worksheet, you might want to check out this lewis and clark worksheet pdf . It’s a great way to learn about the famous explorers and their journey across the United States. And when you’re done with that, you can come back to your air masses and fronts worksheet and finish learning about weather patterns.
Cyclone Formation
When a warm front and a cold front converge, they create a low-pressure area. As air rises within this area, it cools and condenses, releasing heat and energy. This energy fuels the development of a cyclone, a rotating storm system with low atmospheric pressure at its center.
Anticyclone Formation
In contrast, when a cold front and a warm front converge, they create a high-pressure area. As air sinks within this area, it warms and expands, increasing its pressure. This leads to the formation of an anticyclone, a rotating storm system with high atmospheric pressure at its center.
Weather Patterns Associated with Fronts
The passage of different types of fronts brings about distinct weather patterns:
- Warm Fronts:Gradual temperature rise, increased humidity, and steady precipitation (e.g., drizzle, rain).
- Cold Fronts:Rapid temperature drop, decreased humidity, and intense precipitation (e.g., thunderstorms, hail).
- Stationary Fronts:Little temperature change, persistent cloud cover, and intermittent precipitation.
- Occluded Fronts:Complex fronts formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front, bringing a mixture of weather conditions.
Air Masses and Fronts in Weather Forecasting

Understanding air masses and fronts is crucial for accurate weather forecasting. These atmospheric phenomena significantly influence weather patterns, and forecasters rely on tracking their movement and interactions to predict upcoming weather changes.
Weather Maps and Satellite Imagery
Weather maps and satellite imagery are essential tools for monitoring air masses and fronts. Weather maps provide a visual representation of atmospheric conditions, including air pressure, temperature, and wind patterns. Satellite imagery offers valuable information about cloud cover, precipitation, and frontal boundaries.
By analyzing these data, forecasters can identify the location, movement, and characteristics of air masses and fronts. This information helps them predict the likelihood of precipitation, temperature changes, and other weather events.
Query Resolution
What are air masses?
Air masses are large bodies of air that share similar temperature and moisture characteristics, influencing the weather patterns in the regions they occupy.
How do air masses form?
Air masses form over specific source regions, such as oceans, continents, or polar ice caps, acquiring the temperature and moisture properties of the underlying surface.
What are weather fronts?
Weather fronts are boundaries between air masses with contrasting temperatures and densities, leading to the formation of clouds and precipitation.
How do air masses and fronts affect weather?
Air masses and fronts influence weather patterns by bringing changes in temperature, humidity, cloud cover, and precipitation. The interaction between different air masses can result in storms, cyclones, and anticyclones.
Why is it important to understand air masses and fronts?
Understanding air masses and fronts is crucial for weather forecasting, as they provide valuable insights into the movement and behavior of weather systems, enabling meteorologists to predict weather patterns more accurately.