Lesson 3 general use test instruments – Embark on a journey into the realm of test instruments, a world where precision meets practicality. In Lesson 3: General Use Test Instruments, we delve into the fundamentals, applications, and intricacies of these indispensable tools, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the complex world of electrical testing.
Test instruments serve as the eyes and ears of engineers, technicians, and researchers, providing invaluable insights into the behavior of electrical circuits and systems. From oscilloscopes to multimeters, each instrument plays a unique role in troubleshooting, testing, and ensuring the reliability of electronic devices.
Test Instruments Overview
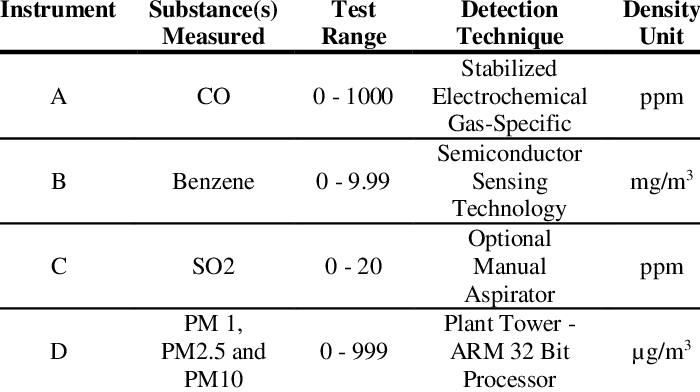
Test instruments are electronic devices used to measure and analyze electrical or physical parameters of a circuit or system. They play a crucial role in various fields, including electrical engineering, electronics, telecommunications, and manufacturing.
Common examples of test instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes, function generators, and spectrum analyzers. Each instrument has specific capabilities and applications. For instance, multimeters measure voltage, current, and resistance, while oscilloscopes display waveforms and analyze signal characteristics.
Importance of Calibration and Maintenance
Calibration and maintenance are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of test instruments. Calibration involves adjusting the instrument’s internal settings to match known standards. This ensures that the instrument provides accurate measurements within its specified range.
Regular maintenance includes cleaning, inspecting, and replacing worn or damaged components. Proper maintenance helps prevent instrument malfunctions, extends its lifespan, and ensures reliable performance.
Types of Test Instruments
Test instruments are essential tools for troubleshooting, diagnosing, and repairing electronic circuits. There are many different types of test instruments, each with its own specific function. Some of the most common types of test instruments include oscilloscopes, multimeters, and signal generators.
The following table provides a summary of the different types of test instruments, their functions, applications, and examples:
| Type | Function | Applications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oscilloscope | Displays a graphical representation of a signal over time | Troubleshooting, diagnosing, and repairing electronic circuits | Tektronix TDS200 Series, Agilent DSO-X 2000A Series |
| Multimeter | Measures voltage, current, and resistance | Troubleshooting, diagnosing, and repairing electronic circuits | Fluke 87V, Fluke 115 |
| Signal generator | Generates electrical signals of various waveforms and frequencies | Testing and calibrating electronic circuits | Agilent 33220A, Tektronix AFG1000 Series |
Applications of Test Instruments

Test instruments play a crucial role in various industries, aiding in troubleshooting, testing, and repair processes. They are indispensable tools for quality control and product development, ensuring the reliability and performance of products.
Electronics Industry
- Troubleshooting:Test instruments help identify and isolate faults in electronic circuits, allowing technicians to diagnose and repair issues efficiently.
- Testing:They verify the functionality of electronic components, such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, ensuring they meet specifications.
- Repair:Test instruments aid in the repair of electronic devices by providing real-time data and measurements, enabling technicians to make informed decisions.
Manufacturing Industry
- Quality Control:Test instruments ensure the quality of manufactured products by verifying compliance with industry standards and specifications.
- Process Monitoring:They monitor production processes in real-time, detecting deviations from optimal conditions and triggering corrective actions.
- Product Development:Test instruments provide valuable data during product development, helping engineers optimize performance and reliability.
Automotive Industry
- Engine Diagnostics:Test instruments help diagnose engine problems by analyzing sensor data, measuring engine performance, and identifying faults.
- Vehicle Inspection:They are used for vehicle inspections, checking safety systems, emissions, and other critical components.
- Repair and Maintenance:Test instruments aid in the repair and maintenance of vehicles, enabling technicians to identify and resolve issues accurately.
Test Instrument Selection
Selecting the right test instrument is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable measurements. Several factors should be considered when making this choice:
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measurement to its true value, while precision indicates the consistency of repeated measurements. High accuracy is essential for applications where precise readings are critical, while high precision is necessary when small variations need to be detected.
Functionality
The functionality of a test instrument determines its capabilities and suitability for specific applications. Consider the types of measurements required, the range of values to be measured, and any special features or functions that may be necessary.
Trade-offs
Different types of test instruments offer varying levels of accuracy, precision, and functionality. It is often necessary to make trade-offs between these factors. For example, a high-accuracy instrument may be less portable or more expensive than a less accurate but more versatile model.
Tips for Choosing the Right Instrument
- Clearly define the measurement requirements and application.
- Research and compare different test instruments based on accuracy, precision, and functionality.
- Consider the cost, portability, and ease of use.
- Consult with experts or manufacturers to seek recommendations.
- Calibrate and maintain the instrument regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Safety Considerations

Ensuring safety is paramount when using test instruments. Electrical equipment and high voltages pose potential hazards that must be addressed to prevent accidents.
Proper grounding and insulation are crucial safety measures. Grounding provides a path for excess electrical current to flow into the earth, minimizing the risk of electrical shock. Insulation prevents electrical current from flowing where it is not intended, protecting users from exposure to live electrical components.
Electrical Hazards, Lesson 3 general use test instruments
- Electrical Shock:Contact with live electrical components can cause severe injury or death. Always verify the power source is disconnected before working on equipment.
- Burns:Electrical current can generate heat, causing burns. Avoid touching exposed electrical connections or components that may be hot.
- Arcing:Arcing occurs when electricity jumps across an air gap, creating a potentially explosive plasma. Keep test leads and equipment away from areas where arcing could occur.
Grounding and Insulation
Grounding and insulation are essential safety measures:
- Grounding:Connect test instruments to a proper earth ground to provide a safe path for electrical current.
- Insulation:Test leads, probes, and other components should be properly insulated to prevent electrical current from flowing where it is not intended.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with test instruments:
- Safety glasses:Protect eyes from flying debris or electrical arcs.
- Gloves:Insulate hands from electrical shock.
- Non-conductive footwear:Prevent electrical current from flowing through the body.
Detailed FAQs: Lesson 3 General Use Test Instruments
What are the most common types of general use test instruments?
Oscilloscopes, multimeters, signal generators, power supplies, and logic analyzers are among the most commonly used general purpose test instruments.
How do I choose the right test instrument for my application?
Consider factors such as accuracy, precision, functionality, and the specific requirements of your testing task.
What are the safety precautions I should take when using test instruments?
Always wear appropriate safety gear, ensure proper grounding, and be aware of potential hazards such as electrical shock and high voltages.