Unveiling the secrets of life, protein synthesis transcription and translation answer key unlocks the intricate mechanisms by which genetic information is transformed into the building blocks of cells. Embark on a journey through the molecular realm, deciphering the steps of transcription and translation, exploring the role of RNA polymerase and ribosomes, and unraveling the genetic code that governs protein synthesis.
Delving deeper, we uncover the intricate regulation of protein synthesis, examining the interplay of transcription factors and post-transcriptional modifications. We investigate errors that can disrupt this delicate process and explore strategies for maintaining its fidelity. Finally, we delve into the remarkable applications of protein synthesis in biotechnology and medicine, pondering the ethical considerations that accompany these transformative technologies.
Protein Synthesis
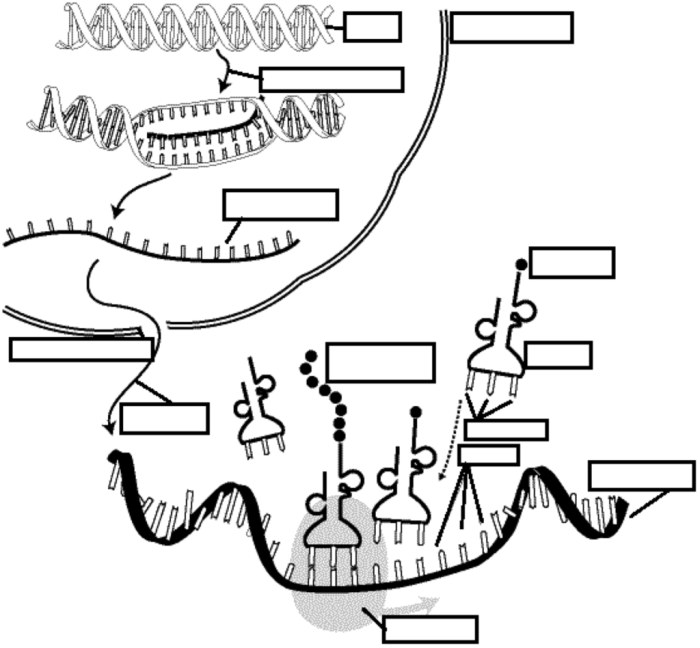
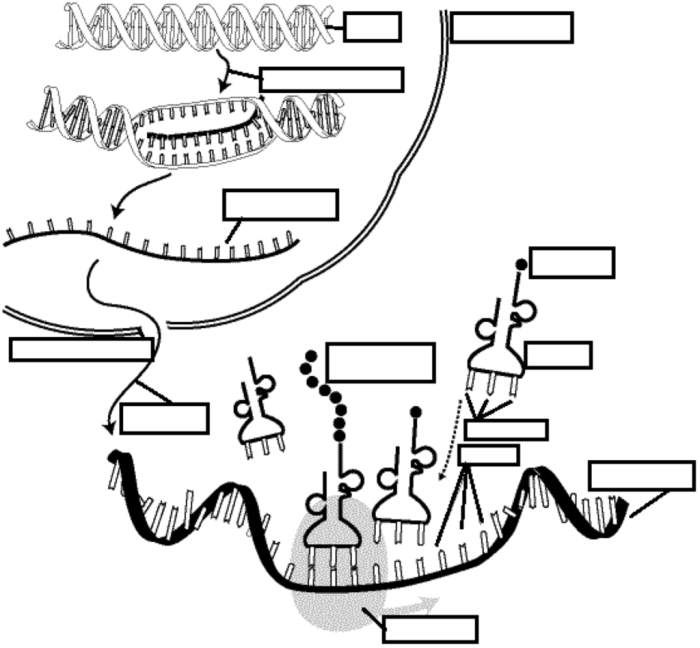
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells produce proteins, which are essential for a wide range of cellular functions. Protein synthesis involves two main steps: transcription and translation.
Transcription Process
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. The key steps involved in transcription are:
- Initiation:RNA polymerase binds to a specific region of DNA called the promoter and begins to separate the DNA strands.
- Elongation:RNA polymerase synthesizes an mRNA molecule by adding complementary nucleotides to the growing mRNA chain.
- Termination:RNA polymerase reaches a specific termination sequence on the DNA and releases the newly synthesized mRNA molecule.
The mRNA molecule is then processed to remove introns (non-coding regions) and add a 5′ cap and a 3′ poly-A tail. These modifications help protect the mRNA molecule from degradation and ensure its efficient translation.
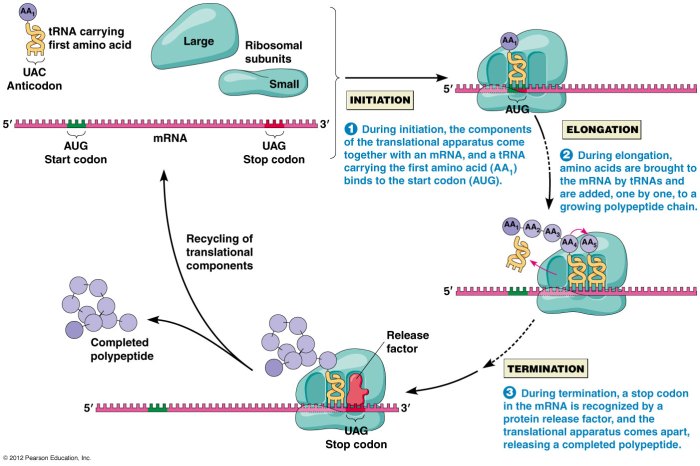
Translation Process, Protein synthesis transcription and translation answer key
Translation is the process of converting the genetic information in mRNA into a protein. The steps of translation are:
- Initiation:The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and reads the start codon (AUG).
- Elongation:The ribosome moves along the mRNA molecule, reading each codon and adding the corresponding amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination:The ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) and releases the newly synthesized protein.
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each codon consists of three nucleotides and codes for a specific amino acid. The genetic code is universal, meaning that it is the same in all living organisms.
Regulation of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is tightly regulated to ensure that cells produce the right proteins at the right time. Transcription factors and other regulatory elements control gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences and either promoting or inhibiting transcription.
Post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications can also regulate protein synthesis. These modifications can affect the stability, localization, and activity of proteins.
Errors in Protein Synthesis
Errors in transcription and translation can lead to the production of non-functional proteins. These errors can be caused by a variety of factors, including mutations in DNA, errors in RNA polymerase, and errors in ribosomes.
Errors in protein synthesis can have a range of effects, from mild to severe. In some cases, errors can lead to the production of proteins that are toxic to cells. In other cases, errors can lead to the production of proteins that are not functional, which can disrupt cellular processes.
Applications of Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is used in a variety of biotechnology and medical applications. For example, protein synthesis is used to produce:
- Therapeutic proteins:Proteins that are used to treat diseases, such as insulin and antibodies.
- Industrial enzymes:Proteins that are used to catalyze chemical reactions in industrial processes.
- Biofuels:Proteins that are used to produce renewable fuels.
Protein synthesis also has potential applications in gene therapy, where it could be used to correct genetic defects or to introduce new genes into cells.
Question Bank: Protein Synthesis Transcription And Translation Answer Key
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix, synthesizes a complementary RNA strand, and elongates it in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
How does the genetic code determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein?
The genetic code is a set of three-nucleotide codons that specify the order of amino acids in a protein. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal.
What are some examples of errors that can occur during protein synthesis?
Errors during protein synthesis can include base substitutions, insertions, deletions, and frameshifts, which can lead to the production of non-functional or truncated proteins.