Lung overexpansion injuries can be caused by – Lung overexpansion injuries, a spectrum of conditions arising from excessive airway pressure, pose significant risks to patients. This article delves into the mechanisms, risk factors, and management strategies associated with lung overexpansion injuries, providing a comprehensive understanding of this critical topic.
Lung Overexpansion Injuries: Causes: Lung Overexpansion Injuries Can Be Caused By
Lung overexpansion injuries arise from excessive distension of lung tissue beyond its normal physiological limits. The primary mechanism underlying these injuries involves an imbalance between airway pressure and lung tissue resistance.
Factors contributing to lung overexpansion injuries include:
- Underlying lung conditions:Weakened or damaged lung tissue, such as in emphysema or asthma, can increase susceptibility to overexpansion.
- External forces:Blunt chest trauma or mechanical ventilation with excessive airway pressure can forcibly overexpand lung tissue.
- Medical interventions:Certain medical procedures, such as bronchoscopy or lung biopsy, may inadvertently introduce excessive airway pressure, leading to overexpansion.
Excessive airway pressure can overwhelm the elastic recoil of lung tissue, causing alveolar overdistension and rupture. This can result in the leakage of air into surrounding tissues, leading to conditions such as pulmonary interstitial emphysema, pneumothorax, or pneumomediastinum.
Types of Lung Overexpansion Injuries
Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema, Lung overexpansion injuries can be caused by
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema occurs when air leaks from the alveoli into the surrounding lung tissue, creating air-filled cysts. This can result from overdistension of alveoli due to excessive airway pressure or underlying lung damage.
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax is the presence of air or gas in the pleural space, the area between the lungs and the chest wall. It can occur when air escapes from the alveoli through a tear or rupture in the lung tissue.
Pneumomediastinum
Pneumomediastinum is the presence of air or gas in the mediastinum, the space between the lungs and the heart. It can occur when air from the lungs or airways dissects into the mediastinum through tears or defects in the mediastinal pleura.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Risk factors for lung overexpansion injuries include:
- Underlying lung disease or damage
- History of chest trauma
- Mechanical ventilation with excessive airway pressure
- Certain medical procedures, such as bronchoscopy or lung biopsy
Preventive measures include:
- Proper ventilation techniques during mechanical ventilation
- Careful monitoring of airway pressure during medical procedures
- Avoiding excessive airway pressure in patients with underlying lung conditions
- Patient education and informed consent regarding potential risks
Diagnosis and Management
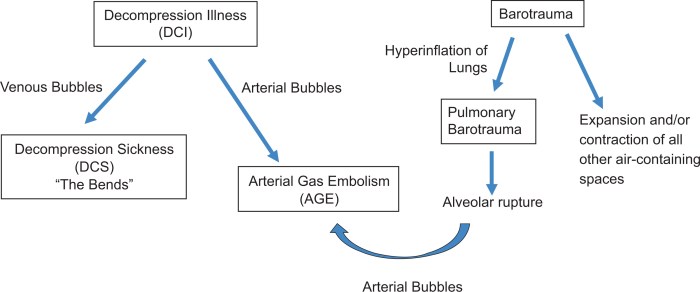
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of lung overexpansion injuries typically involves:
- Physical examination
- Imaging studies, such as chest X-ray or CT scan
Management
Treatment options for lung overexpansion injuries depend on the severity and type of injury:
- Conservative measures:Observation, oxygen therapy, and supportive care may be sufficient for mild cases.
- Surgical interventions:In severe cases, surgical repair of the lung tissue or drainage of the pleural space may be necessary.
Potential complications of lung overexpansion injuries include respiratory distress, infection, and long-term lung damage.
FAQ Insights
What are the common causes of lung overexpansion injuries?
Lung overexpansion injuries can result from various factors, including mechanical ventilation, asthma attacks, and blunt chest trauma.
What are the symptoms of lung overexpansion injuries?
Symptoms may vary depending on the type of injury but commonly include chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing.
How are lung overexpansion injuries diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, imaging studies such as chest X-rays or CT scans, and in some cases, lung function tests.
What are the treatment options for lung overexpansion injuries?
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury and may include conservative measures like oxygen therapy and chest drainage, or surgical interventions in more severe cases.